-
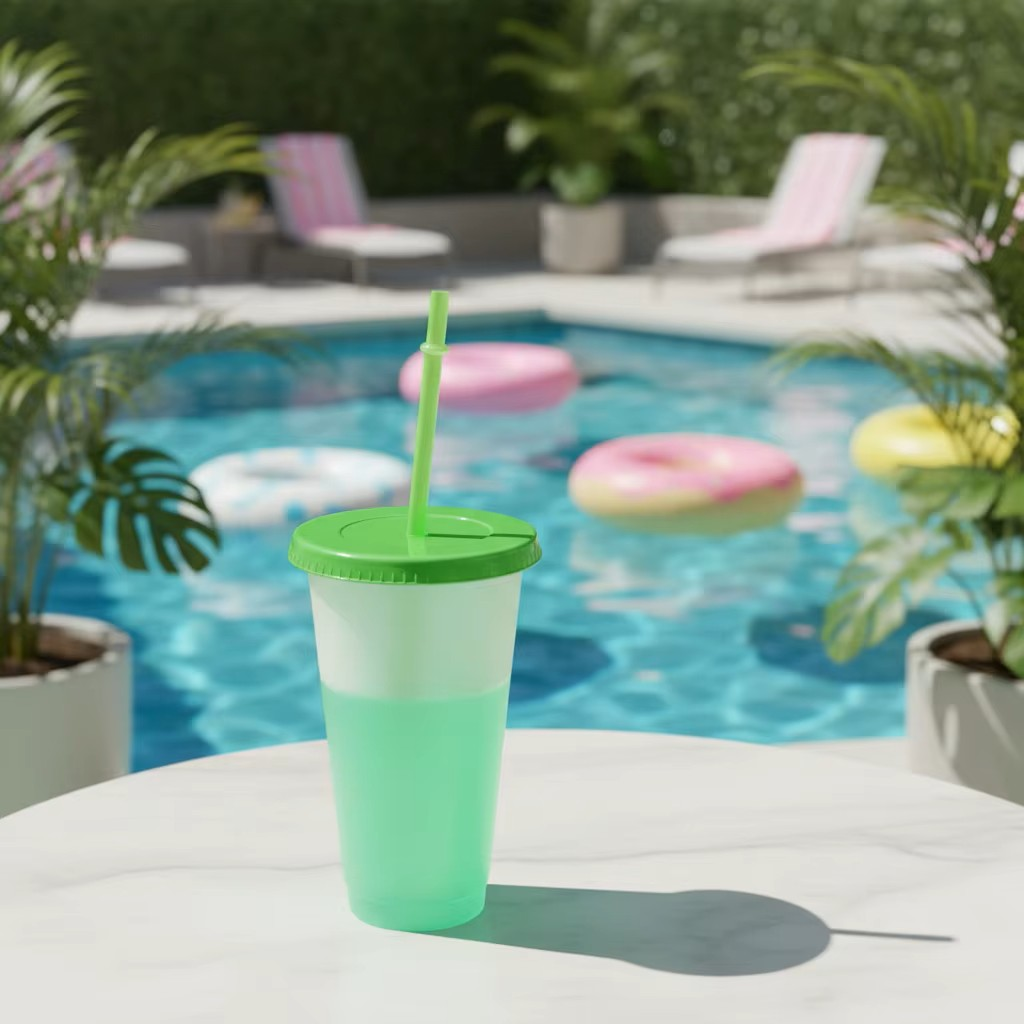

Hot Off the Press! A Bestseller is Born: Suan Houseware Ships Trendsetting Color Changing Cups to Major US Amazon Seller
-
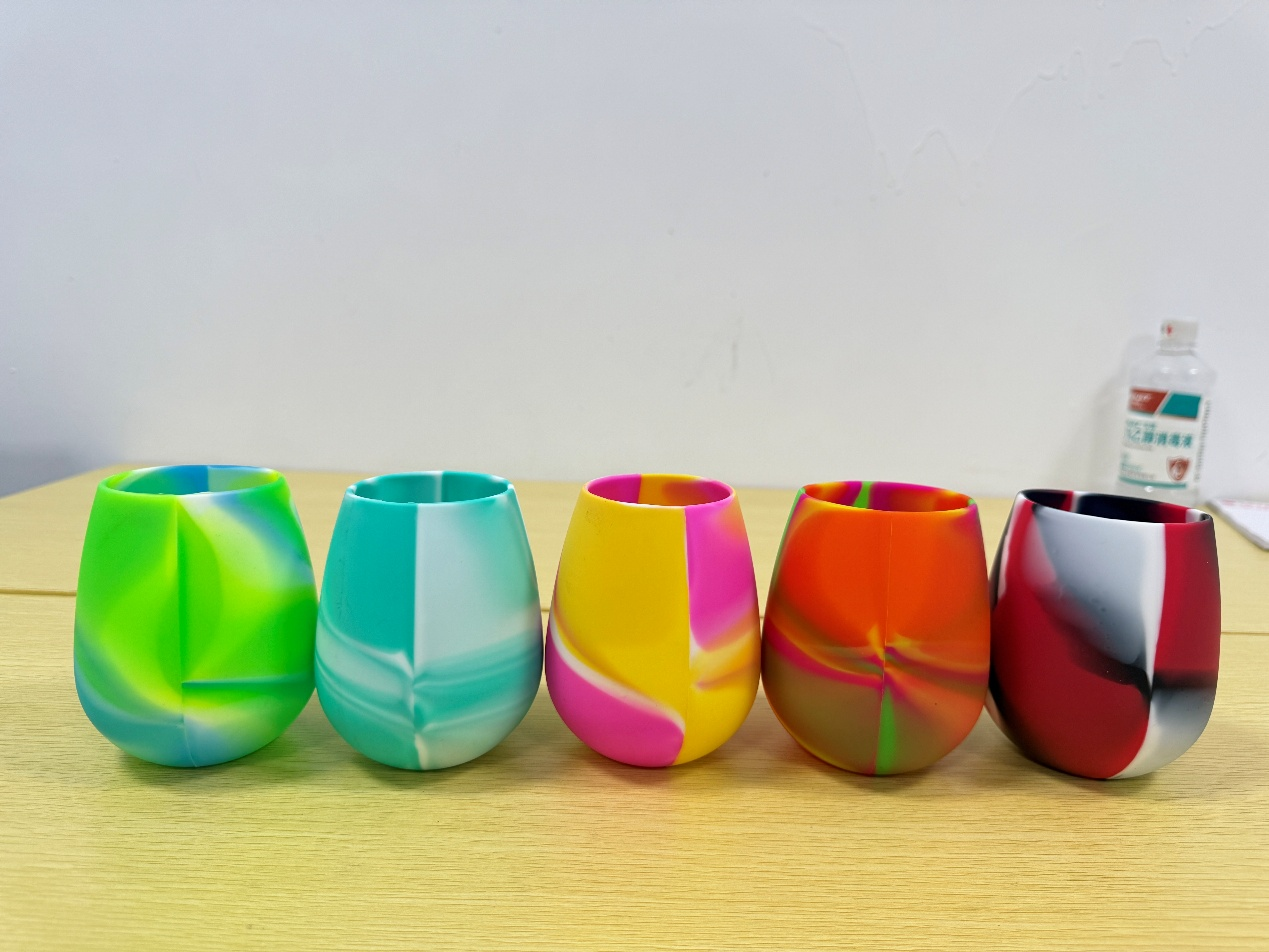

Make Your Mark: Custom Logo Silicone Wine Glass – The Ultimate Party Essential!
-
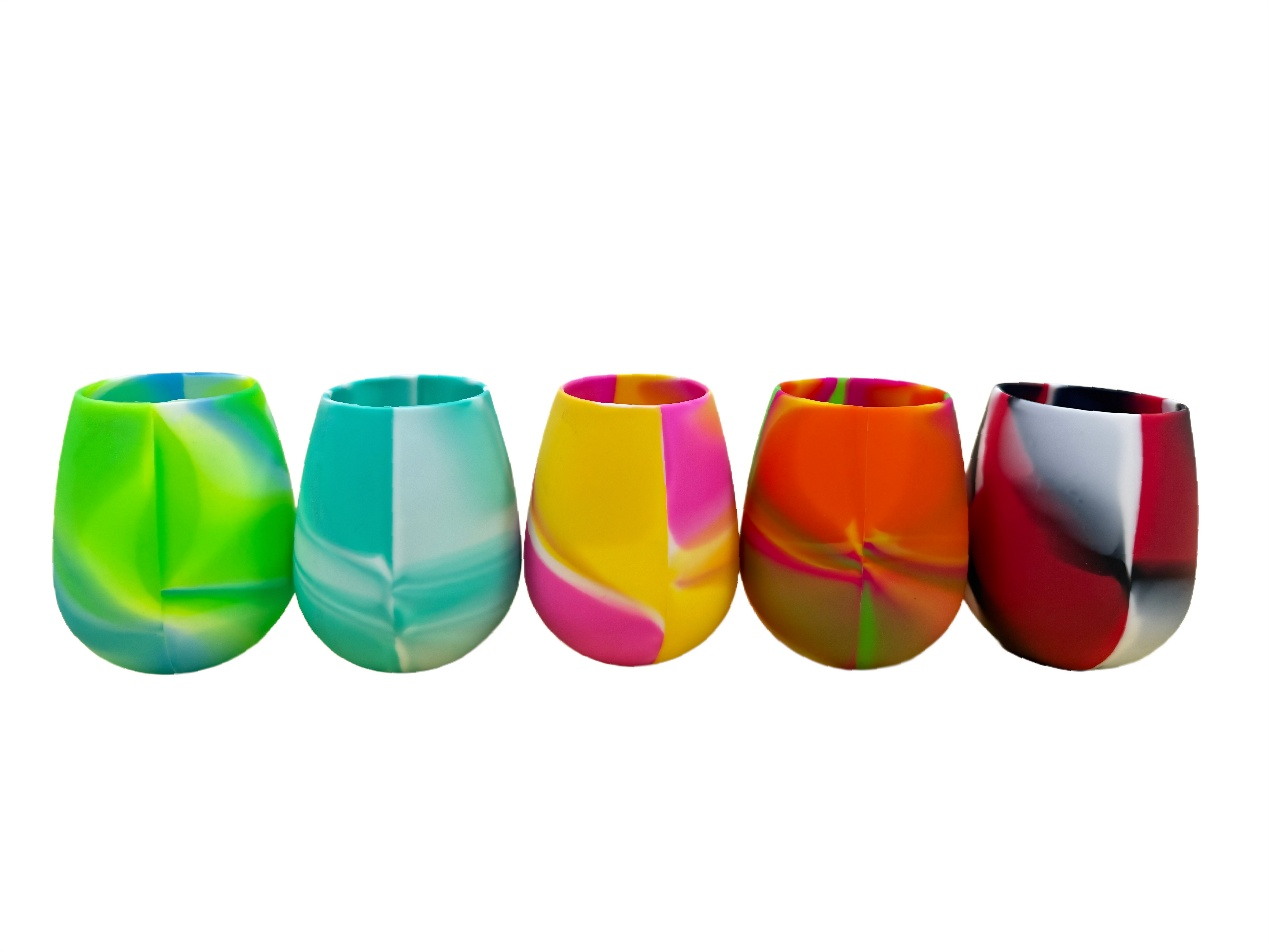

Shatter the Status Quo: Meet the 12oz Silicone Wine Glass That Elevates Every Sip
-

SuanHouse Delivers Premium Glass Spice Jar Sets, Reinforcing Global Supply Capabilities
-

SuanHouse Delivers Custom Silicone Collapsible Cups to Brazilian Law Firm, Highlighting Versatile Branding Solutions
-
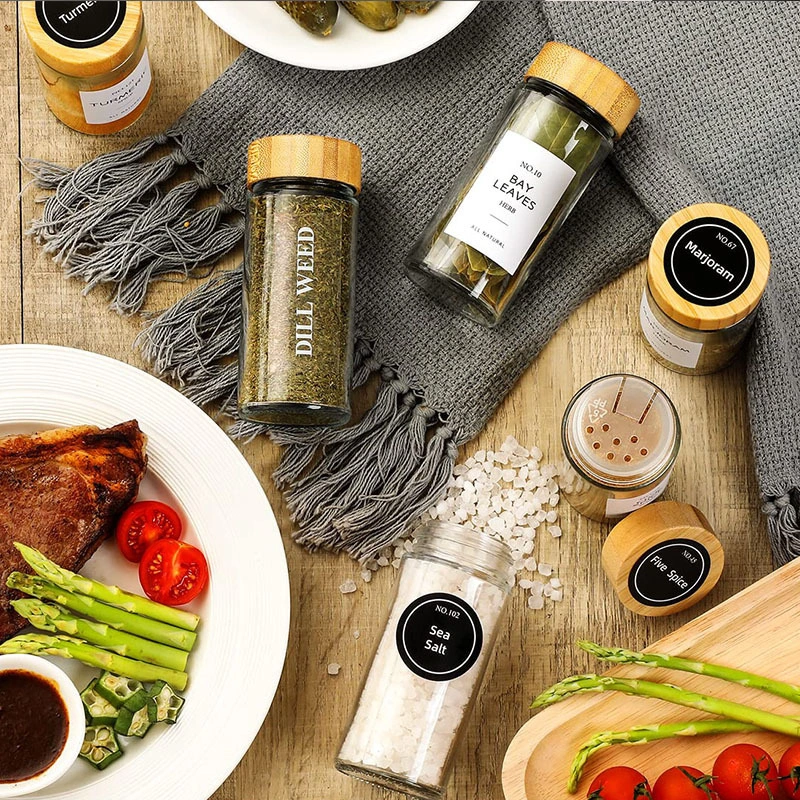

Bamboo Lid Glass Spice Jars: A Comprehensive Product and Market Analysis
-
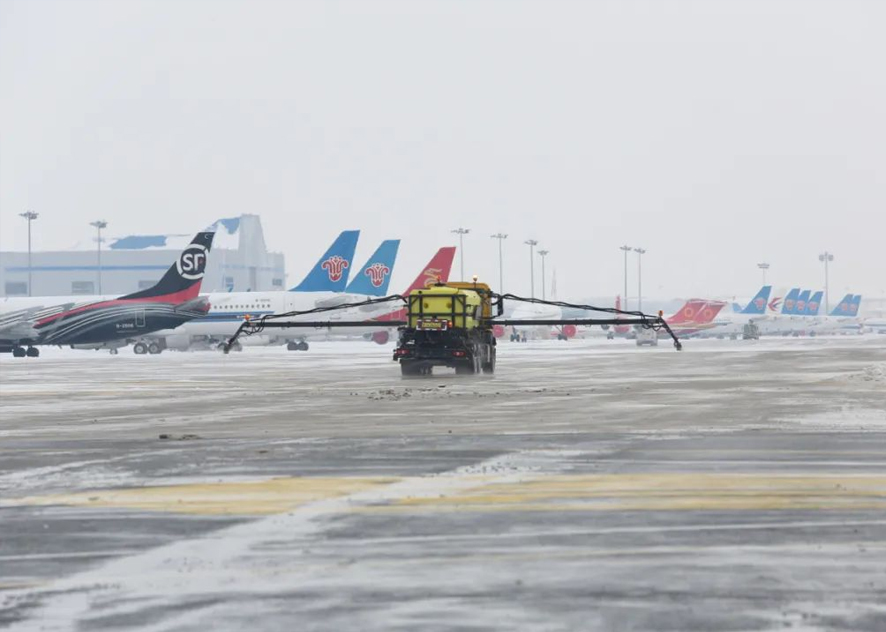

Electric heating tape is used to melt snow at airports
Airport snowmelt is key to maintaining normal airport operations in winter. Under extreme weather conditions, snow-covered runways and aprons can pose huge safety risks for aircraft taking off and landing, seriously endangering the safety of passengers, crew and airport staff. Traditional methods include manual removal and heating equipment, but these methods are inefficient and time-consuming. With the development of science and technology, electric heating tape, as an efficient and energy-saving snow melting equipment, has been widely used in the field of airport snow melting. This article will introduce the principles, advantages and application of electric heating tapes in airport snow melting.
-
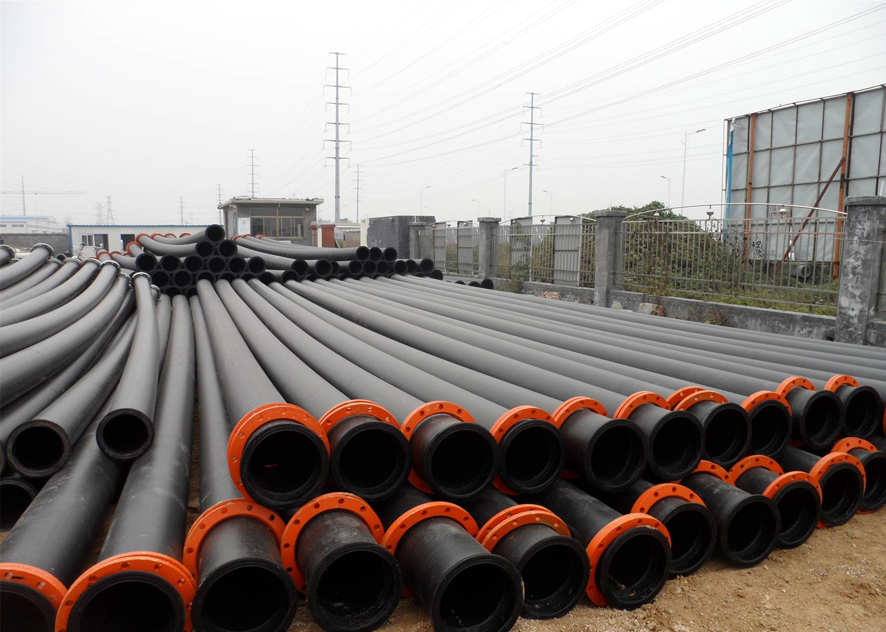

Features of heating tape for plastic pipes
Heating tape is an electric heating device that can be used for insulation and anti-freezing of various pipes. Its working principle is to supplement the heat loss by generating heat from the electric heating wire to maintain the temperature of the material in the pipeline and ensure the normal operation of the pipeline. Plastic pipes are one of the common applications for heating tapes. The following introduces the characteristics of heating tape used in plastic pipes.
-
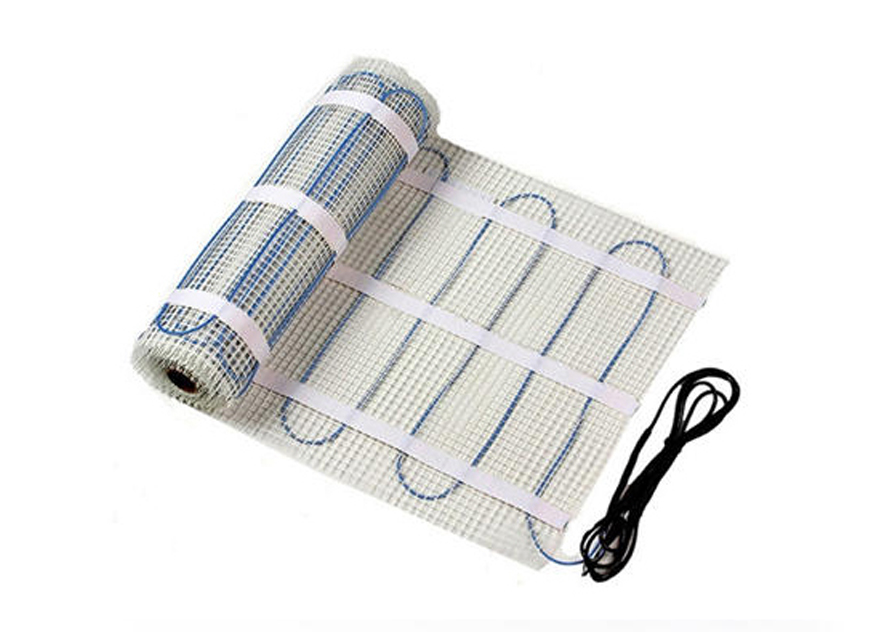

Electric heating tape grid heating mat
Electric heating tape grid heating mat is a new type of heating product. It combines the advantages of electric heating tape and grid heating mat, providing people with an efficient, environmentally friendly and comfortable heating method.
-
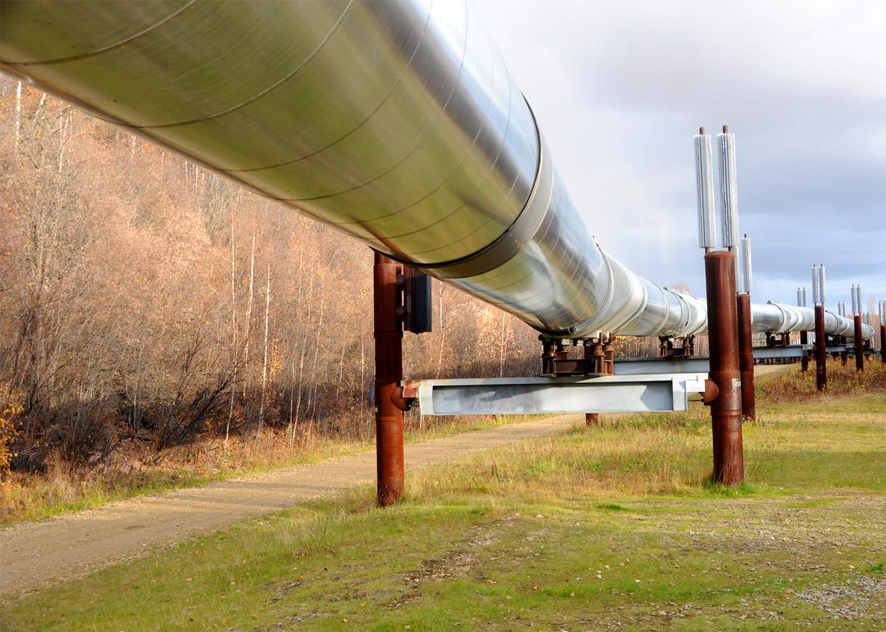

Application of electric heating tape in oil transportation pipelines
With the continuous development and application of science and technology, electric heating tape has become an indispensable part of oil transportation pipelines. The application of electric heating tape not only improves the transportation efficiency of pipelines, but also provides strong support for the development of the petroleum industry.
-
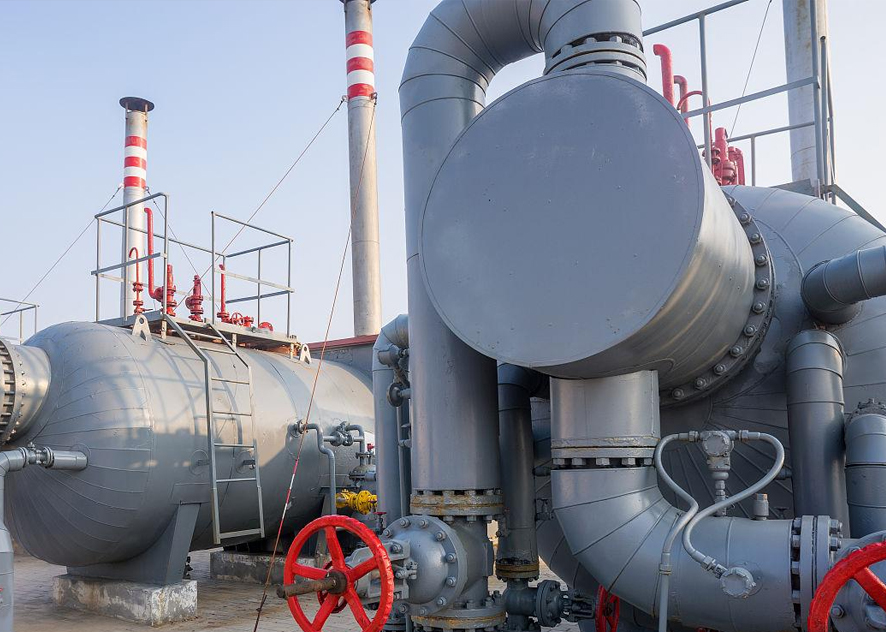

Advantages of electric heat tracing in winter insulation and anti-condensation of chemical plant pipelines
From November 1st to 3rd, the temperature in the central and eastern parts of Northwest China, Inner Mongolia, North China, Northeast China, Huanghuai, Jianghan and other places will drop by 4~8℃, and the temperature in central Inner Mongolia, central Northeast China and other places will drop by more than 10℃. The above-mentioned areas are accompanied by winds of magnitude 4 to 6, with gusts of magnitude 8-9 in central and western Inner Mongolia and other places; some areas in central and western Inner Mongolia, western Gansu, northern Shaanxi and other places have blowing sand or dust weather; the Altay region of Xinjiang, eastern Inner Mongolia, and Heilongjiang Moderate to heavy snowfall, localized blizzards or heavy blizzards occurred in some areas in the central and western regions.
-
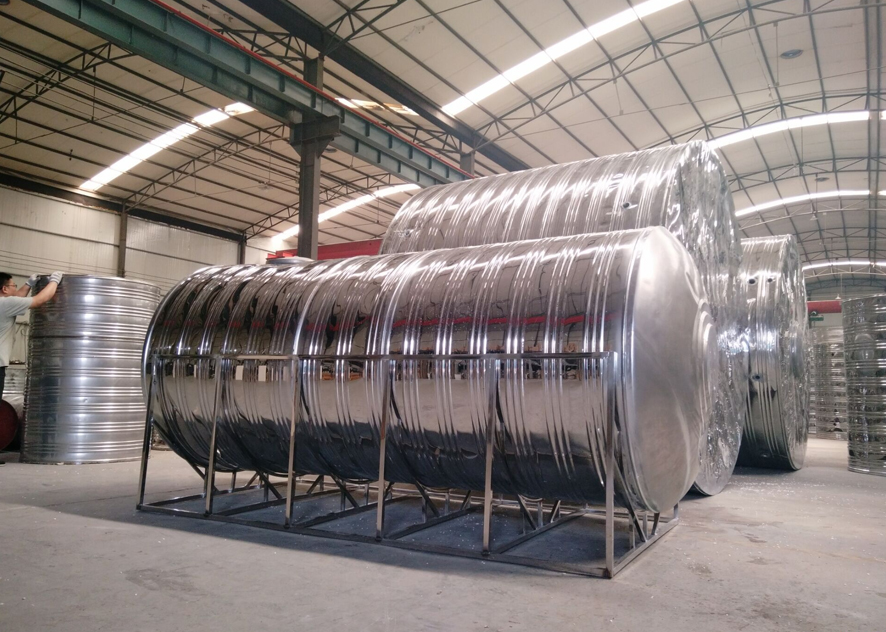

Electric heating is used to prevent freezing of different water tanks
As winter approaches, the temperature gradually drops, and water tanks are one of the indispensable equipment in various industrial and civil fields. However, in low-temperature environments, water tanks are prone to problems such as freezing and cracking, which affects normal use. In order to solve this problem, electric heating technology came into being. The following discusses the application of electric heat tracing in antifreezing water tanks in different scenarios.
-
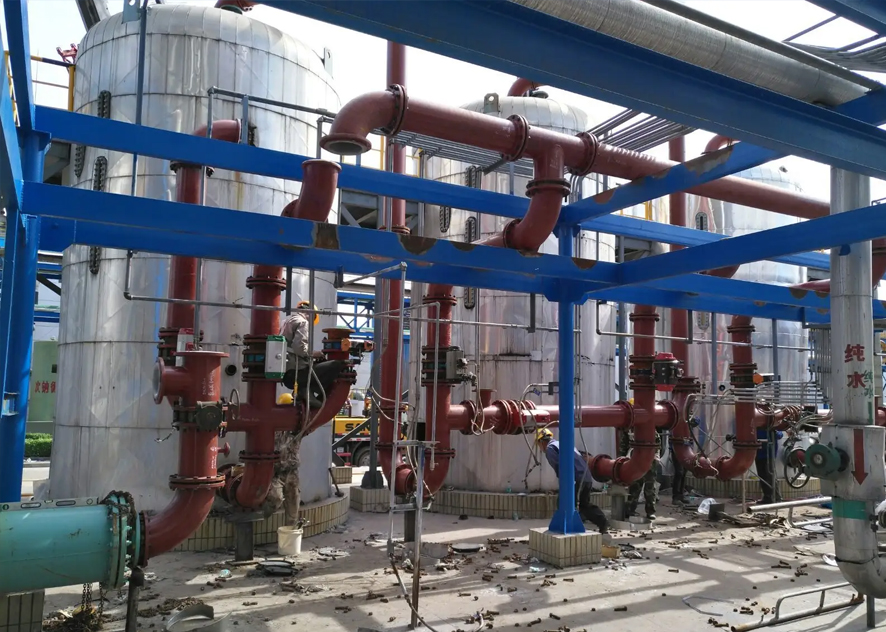

Electric heating tape is used for heating concentrated alkali pipelines
In the fields of petroleum, chemical industry, electric power and other fields, heated pipelines are often needed to meet process requirements. Among them, the heating of concentrated alkali pipelines is a relatively special requirement. Because concentrated alkali is highly corrosive, traditional heating methods cannot meet its needs. As a new type of pipeline heating method, electric heating tape has the advantages of safety, energy saving, environmental protection, etc., making it an ideal choice for heating concentrated alkali pipelines.
-
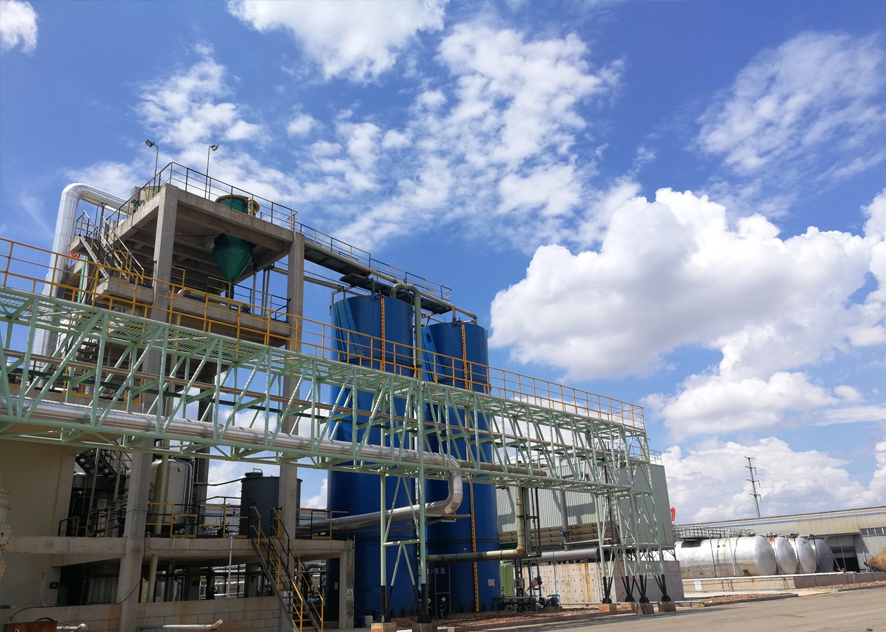

The role of heating tape in power plant flue gas desulfurization
With the development of society and the improvement of environmental awareness, power plant flue gas desulfurization technology has attracted more and more attention. As an effective thermal insulation material, heating tape plays an important role in power plant flue gas desulfurization. The following introduces the role of heating tape in power plant flue gas desulfurization.
-
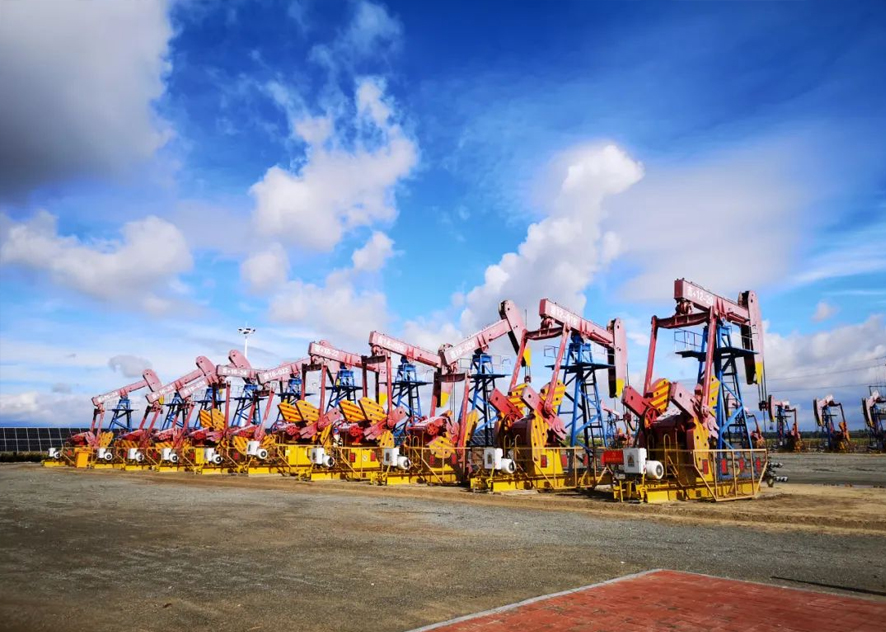

Application of electric heat tracing in petroleum field
With the continuous advancement of science and technology, electric heating technology is increasingly used in the petroleum field. Electric heating technology is a modern technology that uses electrical energy to convert into heat energy to insulate, anti-freeze, anti-corrosion, anti-scale and other treatments for pipelines and equipment. The following is a detailed introduction to the application of electric heat tracing in the petroleum field.
-
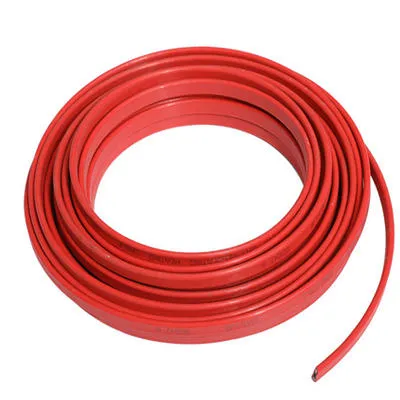

Electric Heating Cable: An Essential Solution for Industrial Pipeline Applications
Electric heating cable is a versatile and indispensable solution for maintaining optimal temperatures in industrial pipelines. With its ability to provide precise and uniform heat distribution, this technology plays a crucial role in various industries, including oil and gas, chemical processing, food and beverage, and many others.
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português русский
русский français
français 日本語
日本語 Deutsch
Deutsch Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Italiano
Italiano Nederlands
Nederlands ไทย
ไทย Polski
Polski 한국어
한국어 Svenska
Svenska magyar
magyar Malay
Malay বাংলা
বাংলা Dansk
Dansk Suomi
Suomi हिन्दी
हिन्दी Pilipino
Pilipino Türk
Türk Gaeilge
Gaeilge عربى
عربى Indonesia
Indonesia norsk
norsk اردو
اردو čeština
čeština Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Українська
Українська Javanese
Javanese فارسی
فارسی தமிழ்
தமிழ் తెలుగు
తెలుగు नेपाली
नेपाली Burmese
Burmese български
български ລາວ
ລາວ Latine
Latine Қазақ
Қазақ Euskal
Euskal Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan slovenský
slovenský Македонски
Македонски Lietuvos
Lietuvos Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel Română
Română Slovenski
Slovenski मराठी
मराठी Српски
Српски 简体中文
简体中文 Esperanto
Esperanto Afrikaans
Afrikaans Català
Català עִברִית
עִברִית Cymraeg
Cymraeg Galego
Galego 繁体中文
繁体中文 Latvietis
Latvietis icelandic
icelandic יידיש
יידיש Беларус
Беларус Hrvatski
Hrvatski Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen Shqiptar
Shqiptar Malti
Malti lugha ya Kiswahili
lugha ya Kiswahili አማርኛ
አማርኛ Bosanski
Bosanski Frysk
Frysk ជនជាតិខ្មែរ
ជនជាតិខ្មែរ ქართული
ქართული ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી Hausa
Hausa Кыргыз тили
Кыргыз тили ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ Corsa
Corsa Kurdî
Kurdî മലയാളം
മലയാളം Maori
Maori Монгол хэл
Монгол хэл Hmong
Hmong IsiXhosa
IsiXhosa Zulu
Zulu Punjabi
Punjabi پښتو
پښتو Chichewa
Chichewa Samoa
Samoa Sesotho
Sesotho සිංහල
සිංහල Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig Cebuano
Cebuano Somali
Somali Точик
Точик O'zbek
O'zbek Hawaiian
Hawaiian سنڌي
سنڌي Shinra
Shinra հայերեն
հայերեն Igbo
Igbo Sundanese
Sundanese Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch Malagasy
Malagasy Yoruba
Yoruba