-

SuanSports National Day Holiday Notice & A Message of Unity Through Sports
-
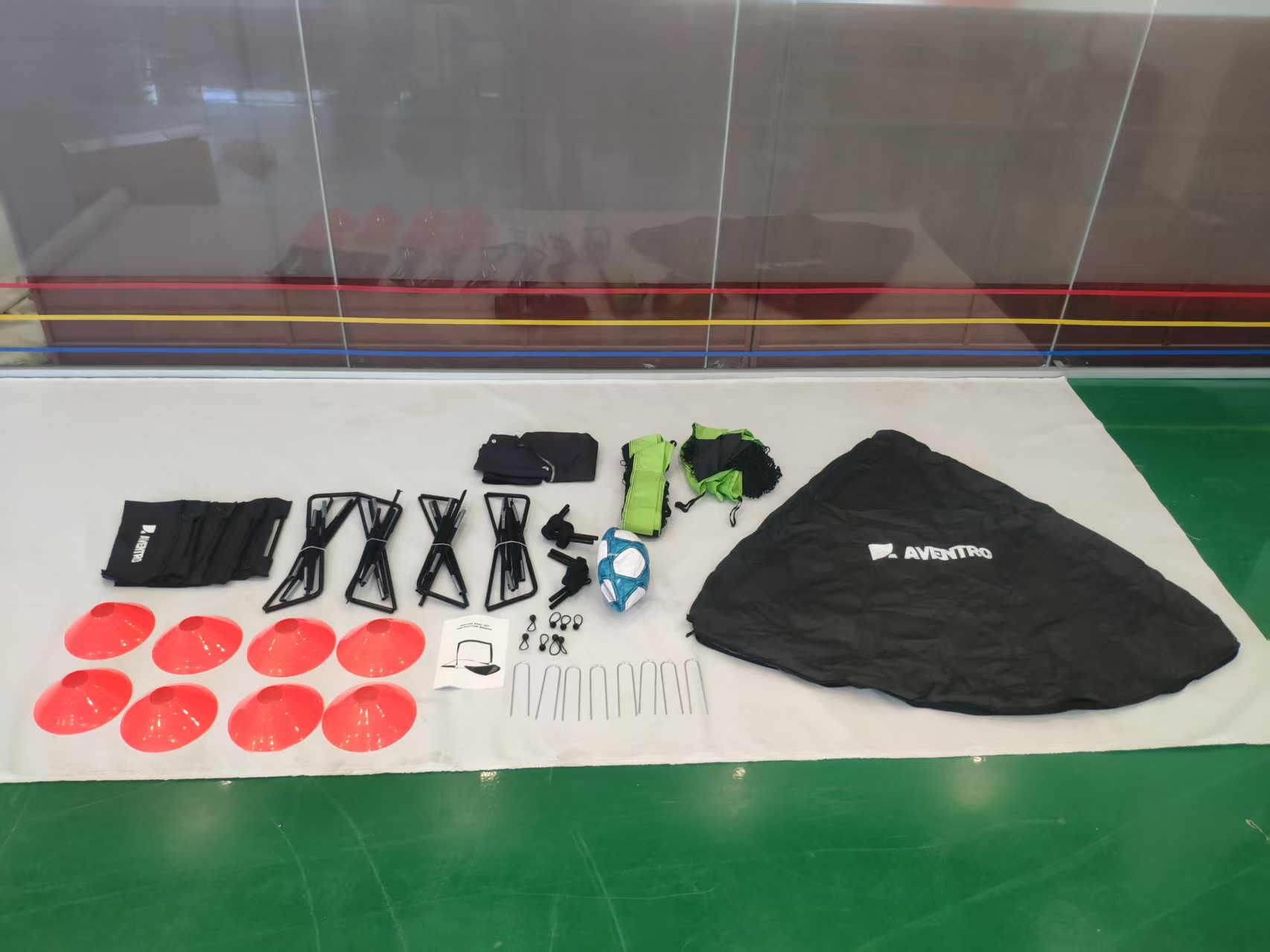

Suan Sports Showcases Customization Excellence with Innovative Foldable Fiberglass Soccer Goal
-
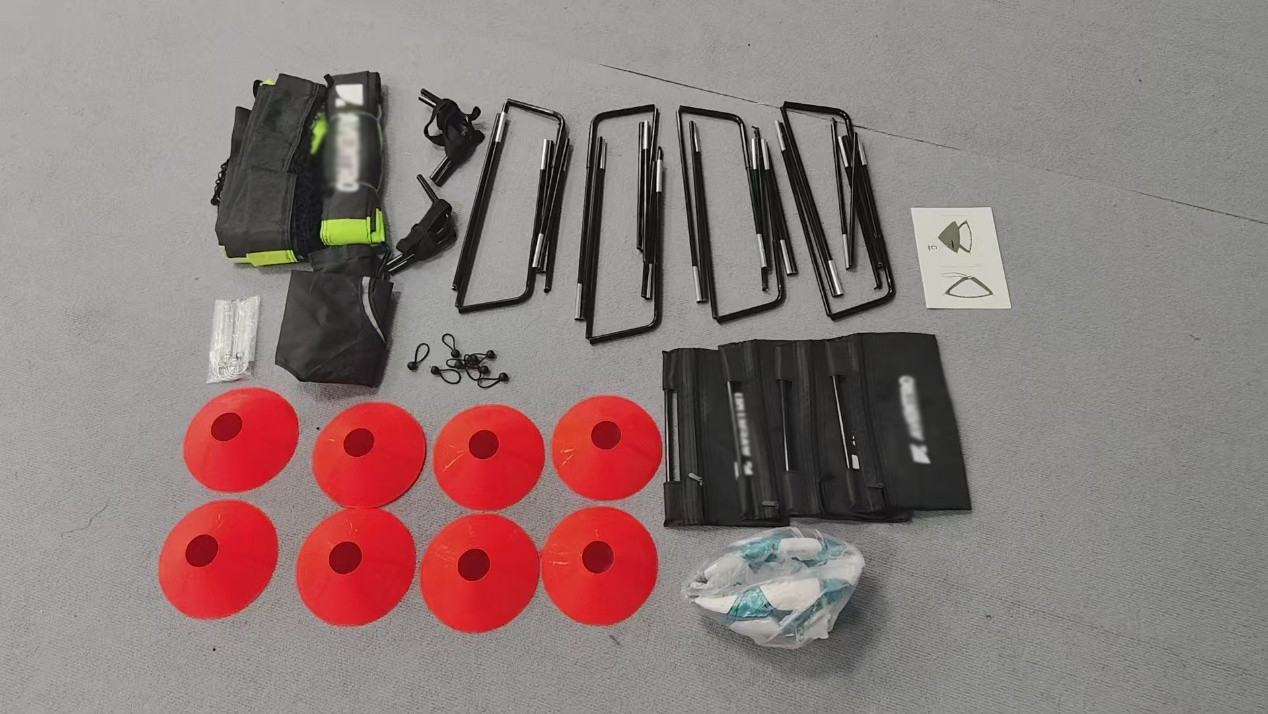

Suan Sports Demonstrates Custom Manufacturing Prowess with Innovative Foldable Soccer Goal
-
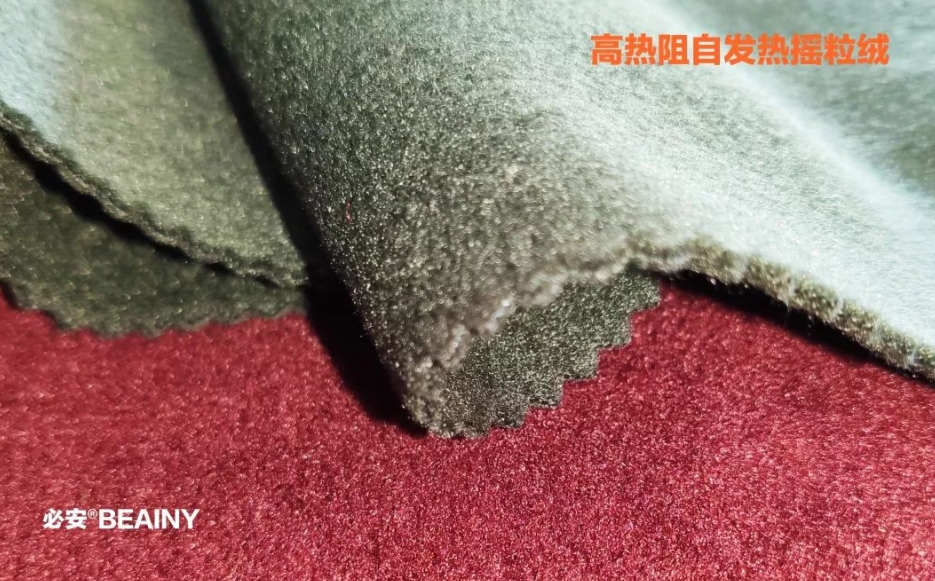

Introduction of polar fleece fabric
-
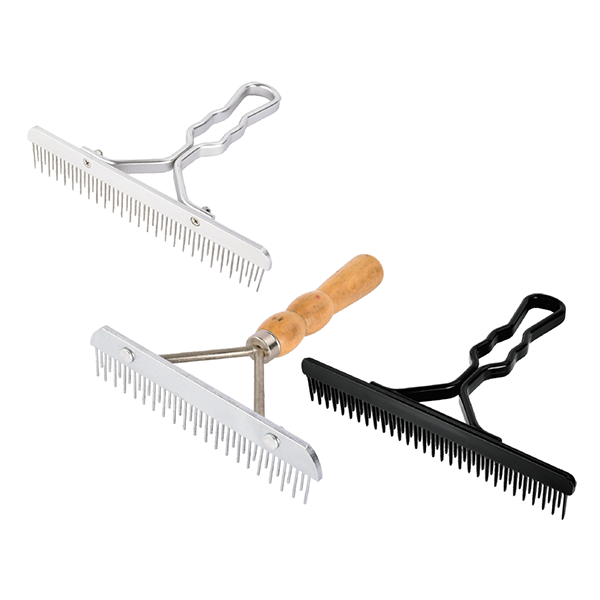

Horse Fluffer Comb Becomes an Essential Tool in Modern Horse Care
-
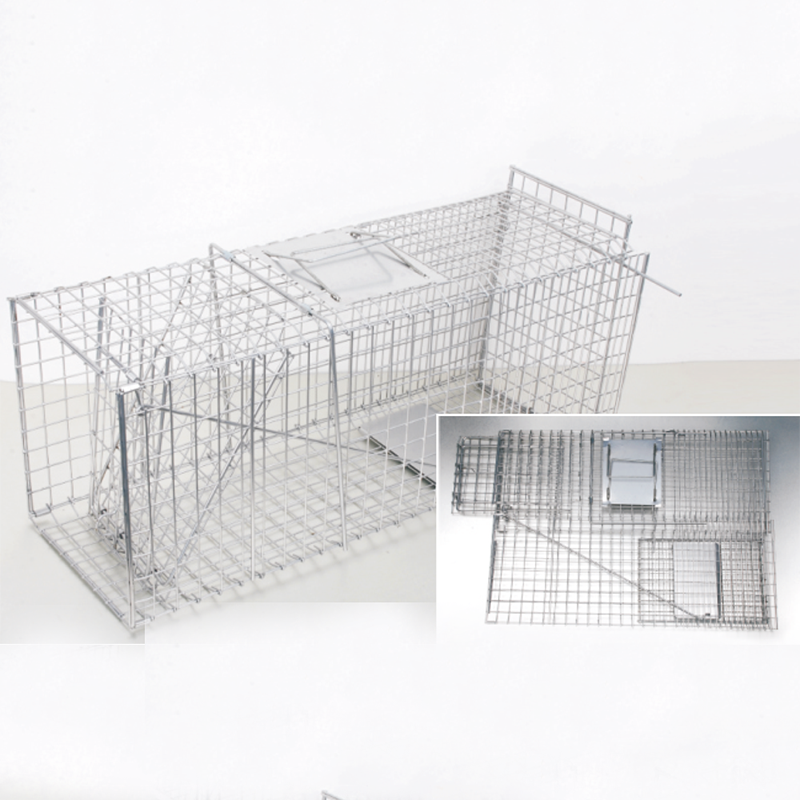
Collapsible Animal Traps Offer Humane and Convenient Wildlife Control
-

Bag dust collector process
Bag dust collector The working principle of a pulse bag dust collector is to enter the dust containing gas into the ash hopper through the air inlet or into the filter bag room through an open flange. The dust containing gas passes through the filter bag as clean gas and enters the clean gas room. It then passes through the exhaust port of the clean gas room and is discharged by the fan. Dust accumulates on the outer surface of the filter bag and continues to increase, causing the resistance of the pulse bag dust collector to continuously increase. In order to ensure that the equipment resistance does not exceed 1200pa and the pulse bag dust collector can continue to work, it is necessary to regularly remove the dust on the filter bag. Ash cleaning is a process in which a pulse valve is activated in a timed sequence controlled by a program, causing compressed air inside the air bag to be sprayed out through the orifice of the blowing tube and induced by a venturi tube to enter the filter bag, causing it to rapidly expand in an instant. With the reverse effect of the airflow, the dust is shaken off to achieve the purpose of ash cleaning.
-

Advantages of Tilting Rotary Furnace
The energy consumption of smelting waste aluminum using a conventional reverberatory furnace is about 1000kw/t, equivalent to 100Nm ³/ Natural gas or 100L/t oil. Using a tilting rotary furnace can save 25%. The decrease in energy consumption is mainly due to the significant improvement of heat transfer in the rotary furnace and the dual channel arrangement of the burners, resulting in a large amount of waste heat recovery in the flue gas. The tilting rotary furnace adopts proportional integral differential control mode (IP) D to control the amount of fuel and combustion air. At the same time, this control is continuous and can automatically adjust the temperature according to the charging amount, making the smelting process in an optimized state. When smelting in a reverberatory furnace, the temperature of the furnace top or upper furnace wall is adjusted to 1100 ℃, while the setting temperature of a tilting rotary furnace is 750 ℃. 25% energy savings come from the improvement of temperature difference and thermal efficiency. The productivity of the tilting rotary furnace is improved by the use of fully automated charging machines, automated slag tanks (boxes), and automated slag removal, which means only simple operations are carried out during the smelting process; The number of operators can be reduced by at least two. One person can operate two furnaces with high thermal efficiency and fully automated control of the smelting process to achieve optimal melting speed. The melting cycle of the tilting rotary furnace can be reduced to less than 4 hours, which means that depending on the furnace capacity, each furnace can melt 6 to 8 furnaces per day, which is equivalent to a 15t furnace melting 90 tons of recycled aluminum every 24 hours, and a 5t furnace can melt about 40 tons. Compared to a reverberatory furnace, a tilting rotary furnace has a much wider range of waste capacity, and can effectively melt from low-level slag, chips, and cans to process waste. Therefore, recycled aluminum enterprises can use low-level waste to smelt higher grade or even recycled aluminum, achieving good economic benefits. Low quality waste materials such as chips and slag cannot be melted using a reverberatory furnace. From the above introduction, it can be seen that the main advantages of tilting rotary furnaces are reduced burning loss and increased productivity, which is due to the comprehensive automation control of melting temperature, time, and combustion parameters.
-
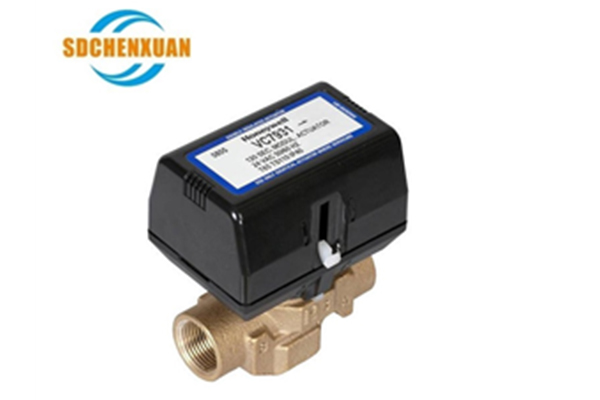

VC7931 Series Regulator Type Fan Coil Electric Valve Delisting Notices Of Some Products
In order to better lifecycle management of regulator type fan coil electric valve product, delisting plan of VC7931 series nine models regulator type fan coil electric valve.
-

What are the cathode and anode materials for electrolytic lead, and what are the specific reactions?
The anode is made of coarse or semi refined lead, the cathode is made of pure lead, and the electrolyte is composed of silicofluoric acid and lead silicofluoric acid. Anode: Lead is oxidized into lead ions and enters the solution: Pb-2e=Pb2+; Cathode: Lead ions in the solution are reduced to metal lead and precipitated: Pb2++2e=Pb. During the electrolysis process, impurities such as iron, zinc, tin, nickel, diamond, and other metals with a lower standard electrode potential than lead dissolve into the solution together; Metals with standard electrode potentials corrected for lead, such as antimony, arsenic, pound, copper, tin, gold, and silver, do not dissolve and form anode slime, which adheres to the anode surface. Electrolysis is the process of causing oxidation-reduction reactions on the cathode and anode by passing current through an electrolyte solution or molten electrolyte (also known as electrolyte). Electrochemical cells can undergo electrolysis under an applied DC voltage. The process of chemical changes caused by the passage of an electric current through a substance.
-

What is ingot mold
An ingot mold is a container or mold used in the casting process to shape and solidify molten metal into ingots. It is typically made of durable materials such as cast iron, steel, or graphite, and is designed to withstand the high temperatures and pressures involved in the casting process.
-

Working Principle of Eddy Current Sorter
Eddy current sorting is a sorting technique that utilizes different conductivity of materials. Its sorting principle is based on two important physical phenomena: an alternating magnetic field that changes over time is always accompanied by an alternating electric field (electromagnetic induction law); A current carrying conductor generates a magnetic field (Biot Savart's law).
-

Smelting and classification of lead
01. Lead smelting The main raw materials for lead smelting are lead sulfide concentrate and a small amount of block ore. There are two methods for smelting lead: pyrometallurgy and wet metallurgy. Currently, pyrometallurgy is the main method in the world, and wet metallurgy of lead is still in the experimental research stage. The pyrometallurgical lead smelting process basically adopts the sintering roasting blast furnace smelting process, accounting for 85-90% of the total lead production; Next is the reaction melting method, which can be equipped with chamber furnaces, short kilns, electric furnaces, or vortex furnaces; Precipitation melting is rarely used. The refining of lead mainly adopts fire refining, followed by electrolytic refining, but due to customary reasons, electrolytic refining is not widely used in China. For difficult to separate sulfide lead zinc mixed concentrates, the closed blast furnace smelting method that simultaneously produces lead and zinc is generally used for processing. For the extremely difficult to separate mixed ore of lead and zinc oxide, a unique treatment method has been developed in China through long-term research, which involves using the raw ore or its enriched products of the mixed ore of lead and zinc oxide, sintering or pelletizing them, and melting them in a blast furnace to obtain coarse lead and molten slag containing lead and zinc. The slag is further fumigated in a fuming furnace to obtain zinc oxide products, and electrolytic zinc is obtained through wet zinc smelting. In addition, zinc oxide products can also be directly fumigated using a rotary kiln.
-

The Use of Lead and Zinc
Lead and zinc are widely used in fields such as electrical industry, mechanical industry, military industry, metallurgical industry, chemical industry, light industry, and pharmaceutical industry. In addition, lead metal has many uses in sectors such as the nuclear industry and petroleum industry. More than 80% of the world's lead is used to produce lead-acid batteries.
-

Battery dismantling machines
Battery dismantling machines Battery dismantling machines (battery dismantling machines, battery dismantling machines) easily disassemble waste batteries. If electric vehicle batteries and car batteries are directly disposed of, they pose a significant risk and require centralized recycling for harmless treatment. Therefore, we will use our company's waste battery dismantling machine. The battery car battery dismantling machine equipment uses manual feeding to push waste batteries into the body. The propulsion system pushes the batteries into the position to be cut, and the crank drives the cutting blade to accurately cut off the waste battery cover. The cutting blade can be adjusted, and the propulsion system pushes the next battery forward again.
-
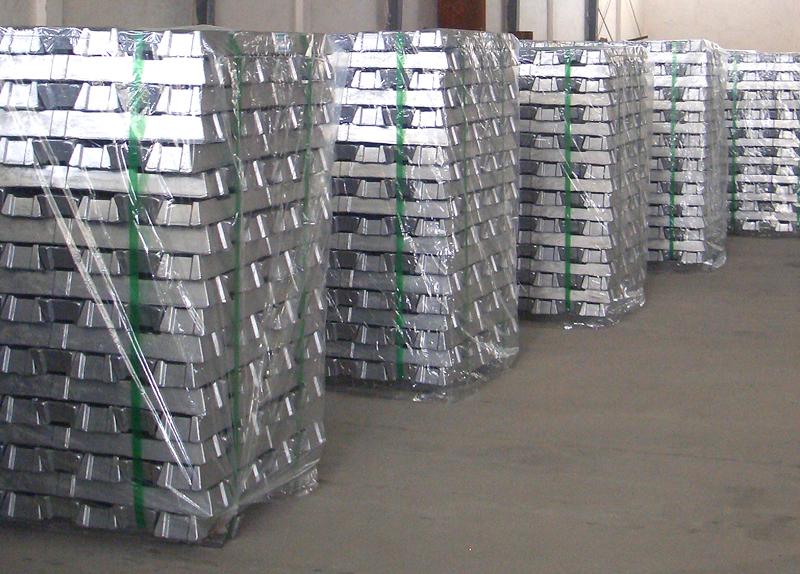

How many models of aluminum ingots are there
According to the national standard, aluminum ingots can be divided into 8 models according to their composition, AI99.90 85 70 60 50 00 7E. The general market demand is for standard aluminum AI99.70, with high-end requirements of 85, special requirements of 99.90, and even a few higher requirements.
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português русский
русский français
français 日本語
日本語 Deutsch
Deutsch Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Italiano
Italiano Nederlands
Nederlands ไทย
ไทย Polski
Polski 한국어
한국어 Svenska
Svenska magyar
magyar Malay
Malay বাংলা
বাংলা Dansk
Dansk Suomi
Suomi हिन्दी
हिन्दी Pilipino
Pilipino Türk
Türk Gaeilge
Gaeilge عربى
عربى Indonesia
Indonesia norsk
norsk اردو
اردو čeština
čeština Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Українська
Українська Javanese
Javanese فارسی
فارسی தமிழ்
தமிழ் తెలుగు
తెలుగు नेपाली
नेपाली Burmese
Burmese български
български ລາວ
ລາວ Latine
Latine Қазақ
Қазақ Euskal
Euskal Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan slovenský
slovenský Македонски
Македонски Lietuvos
Lietuvos Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel Română
Română Slovenski
Slovenski मराठी
मराठी Српски
Српски 简体中文
简体中文 Esperanto
Esperanto Afrikaans
Afrikaans Català
Català עִברִית
עִברִית Cymraeg
Cymraeg Galego
Galego 繁体中文
繁体中文 Latvietis
Latvietis icelandic
icelandic יידיש
יידיש Беларус
Беларус Hrvatski
Hrvatski Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen Shqiptar
Shqiptar Malti
Malti lugha ya Kiswahili
lugha ya Kiswahili አማርኛ
አማርኛ Bosanski
Bosanski Frysk
Frysk ជនជាតិខ្មែរ
ជនជាតិខ្មែរ ქართული
ქართული ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી Hausa
Hausa Кыргыз тили
Кыргыз тили ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ Corsa
Corsa Kurdî
Kurdî മലയാളം
മലയാളം Maori
Maori Монгол хэл
Монгол хэл Hmong
Hmong IsiXhosa
IsiXhosa Zulu
Zulu Punjabi
Punjabi پښتو
پښتو Chichewa
Chichewa Samoa
Samoa Sesotho
Sesotho සිංහල
සිංහල Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig Cebuano
Cebuano Somali
Somali Точик
Точик O'zbek
O'zbek Hawaiian
Hawaiian سنڌي
سنڌي Shinra
Shinra հայերեն
հայերեն Igbo
Igbo Sundanese
Sundanese Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch Malagasy
Malagasy Yoruba
Yoruba