Ironmaking blast furnaces are commonly known as blast furnaces; The blast furnace generally refers to a vertical furnace for smelting non-ferrous metals.
- The blast furnace can be used for matte smelting of metals such as copper, nickel, cobalt, and reduction smelting of metals such as lead and zinc. It can also be used for melting miscellaneous copper and processing other materials. The charge of a blast furnace is generally block shaped, and the fuel is coke. The cross-section of the blast furnace body is mostly rectangular, while small furnaces are generally circular or elliptical.
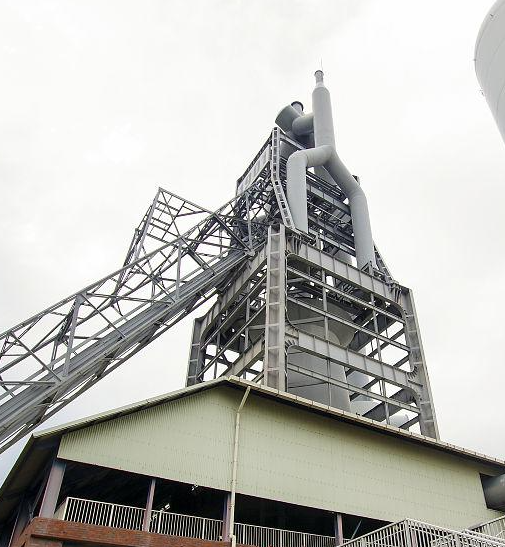

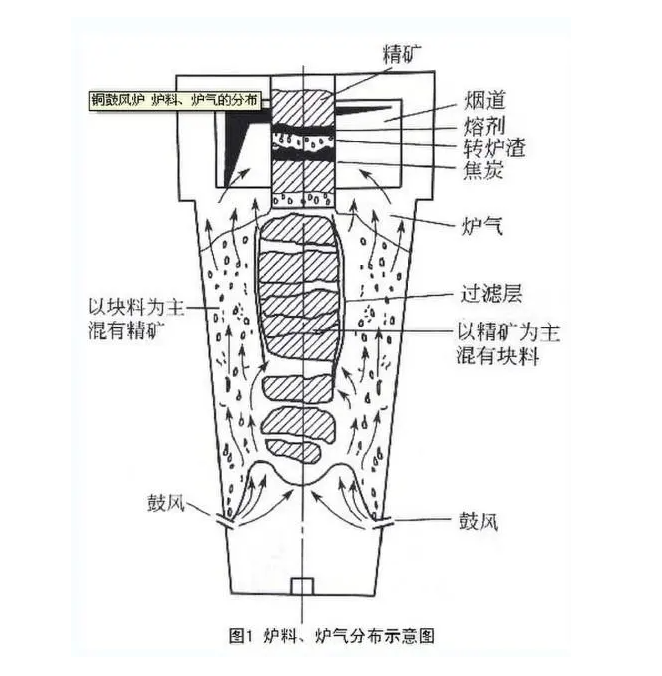
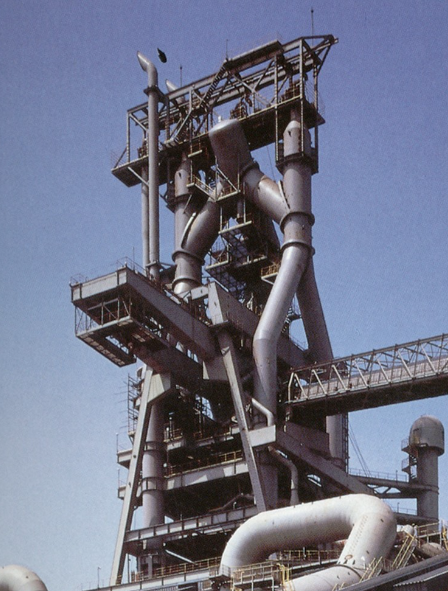
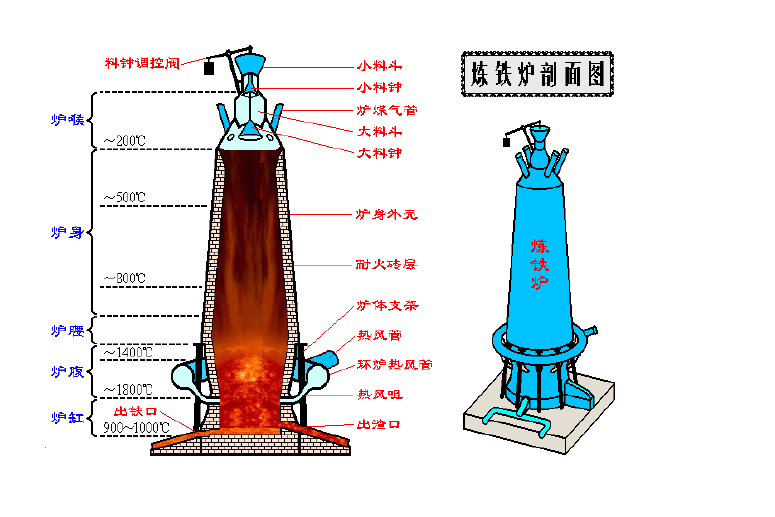
2. A circular iron making vertical furnace with a steel plate shell and a refractory brick lining inside. The main body of the blast furnace is divided from top to bottom into five parts: throat, shaft, waist, bosh, and hearth. Install charging equipment above the furnace throat (see the blast furnace feeding and charging system). The upper part of the furnace hearth is uniformly equipped with air vents along the circumference, and hot air is blown into the furnace through the air vent through the hot air enclosure, branch pipes, elbows, and direct blowing pipes (see blast furnace blowing system). There is a slag outlet below the air outlet plane, and an iron tapping hole below the slag outlet plane.
 English
English Español
Español Português
Português русский
русский français
français 日本語
日本語 Deutsch
Deutsch Tiếng Việt
Tiếng Việt Italiano
Italiano Nederlands
Nederlands ไทย
ไทย Polski
Polski 한국어
한국어 Svenska
Svenska magyar
magyar Malay
Malay বাংলা
বাংলা Dansk
Dansk Suomi
Suomi हिन्दी
हिन्दी Pilipino
Pilipino Türk
Türk Gaeilge
Gaeilge عربى
عربى Indonesia
Indonesia norsk
norsk اردو
اردو čeština
čeština Ελληνικά
Ελληνικά Українська
Українська Javanese
Javanese فارسی
فارسی தமிழ்
தமிழ் తెలుగు
తెలుగు नेपाली
नेपाली Burmese
Burmese български
български ລາວ
ລາວ Latine
Latine Қазақ
Қазақ Euskal
Euskal Azərbaycan
Azərbaycan slovenský
slovenský Македонски
Македонски Lietuvos
Lietuvos Eesti Keel
Eesti Keel Română
Română Slovenski
Slovenski मराठी
मराठी Српски
Српски 简体中文
简体中文 Esperanto
Esperanto Afrikaans
Afrikaans Català
Català עִברִית
עִברִית Cymraeg
Cymraeg Galego
Galego 繁体中文
繁体中文 Latvietis
Latvietis icelandic
icelandic יידיש
יידיש Беларус
Беларус Hrvatski
Hrvatski Kreyòl ayisyen
Kreyòl ayisyen Shqiptar
Shqiptar Malti
Malti lugha ya Kiswahili
lugha ya Kiswahili አማርኛ
አማርኛ Bosanski
Bosanski Frysk
Frysk ជនជាតិខ្មែរ
ជនជាតិខ្មែរ ქართული
ქართული ગુજરાતી
ગુજરાતી Hausa
Hausa Кыргыз тили
Кыргыз тили ಕನ್ನಡ
ಕನ್ನಡ Corsa
Corsa Kurdî
Kurdî മലയാളം
മലയാളം Maori
Maori Монгол хэл
Монгол хэл Hmong
Hmong IsiXhosa
IsiXhosa Zulu
Zulu Punjabi
Punjabi پښتو
پښتو Chichewa
Chichewa Samoa
Samoa Sesotho
Sesotho සිංහල
සිංහල Gàidhlig
Gàidhlig Cebuano
Cebuano Somali
Somali Точик
Точик O'zbek
O'zbek Hawaiian
Hawaiian سنڌي
سنڌي Shinra
Shinra հայերեն
հայերեն Igbo
Igbo Sundanese
Sundanese Lëtzebuergesch
Lëtzebuergesch Malagasy
Malagasy Yoruba
Yoruba